Simple Present Tense (Present Indefinite Tense) – Rules, Examples, and Exercises. Use of Simple Present tense, Learn how to make and use Simple Present Tense Sentences in English Grammar. This lesson is useful for those who are learning English. It is used to express the actions of the present time. You can also review the Present Indefinite Tense Examples, rules, and exercises.
What is the Simple Present Tense?
Simple Present Tense is used to express the general time actions, repeated actions or habits, universal truth, and future. It is also called the Present Indefinite Tense. For Example:
- She runs.
- They play.
- I run there.
- We are honest.
- The man is not sure.
Note: The base form of the verb is used to form simple present tense. If the subject is singular, ‘s or es‘ is added to the main verb.

Simple Present Tense Rules and Examples
Structure: Subject + verb + object + other words
Helping Verbs – Do, Does
Main Verb – Verb I (Base Form)
Rules for Simple/Affirmative Sentences:
- We do not use Helping Verbs (Auxiliary Verbs) in simple or affirmative sentences.
- We add ‘s’ or ‘es’ to the main verb for the 3rd person singular (he, she, it, or Singular Countable Noun).
- For the verb to be (is, am, are), we do not use an auxiliary (do, does), even for questions and negatives.
- We add ‘es‘ to the main verb if there are s, ss, sh, ch, o, x, z in the last.
- Go – Goes, Rush – Rushes, Do – Does, Watch – Watches
- If there is a consonant before ‘y’ in the main verb, we add ‘ies‘ by removing ‘y
- Fly – Flies, Cry – Cries, Fry – Fries
- If there is a vowel before the – y:
- play –> plays, pray –> prays,
Exception – does, goes
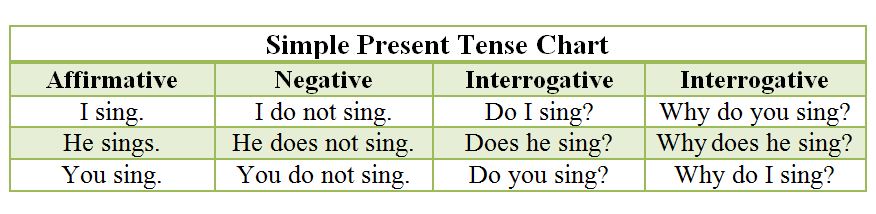
Simple Present Tense Chart
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
| I sing. | I do not sing. | Do I sing? |
| He sings. | He does not sing. | Does he sing? |
| You sing. | You do not sing. | Do you sing? |
Simple/Affirmative Sentences
The structure of an affirmative sentence is very simple. First of all, we put ‘Subject’ or ‘Noun’ or ‘Pronoun’ of the sentence. The base form of the verb is used after the subject. It is also called the ‘Main Verb’. The Simple Present Tense Sentence Structure is given below:
Structure – Subject + Verb + Object + Other Words
Examples –
- He sings a song.
- She drives a car.
- It rains daily.
- Jack writes an essay.
- I read a book every week.
- You go for a walk in the evening.
- We fly kites daily.
- They ride their bikes.
- The girls play hockey.
- My friends come to meet me on Sunday.
- The workers of this factory come on time.
- I want to study abroad.
Modal Auxiliary Verbs Exercises with Answers
Simple Present Tense of the verb ‘To be’
The verb ‘to be’ is used in the simple present tense to express the condition, fact, or general information. The forms of the verb ‘to be’ are used.
Form of the to be
- is
- am
- are
‘Is, am, and are‘ used to make the simple present tense. They are also used in the present continuous tense.
Structure for Verb To Be – Subject + to be (is/am/are) + noun/adjective
Examples –
- He is a doctor.
- She is a lawyer.
- It is a chair.
- John is a teacher.
- I am a doctor.
- We are the police officers.
- You are a director of Hollywood.
- They are players of cricket.
- The boys are free.
- The girls of this city are talented.
Read also:
- Parts of Speech Exercises with answers
- Noun Exercises with Answers
- 100 sentences of simple present tense in Hindi
- Affirmative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense
Rules for Negative Sentences –
Negative Sentences Structure and Rules of Simple Present Tense are given below:
- We don’t add ‘s or es‘ to the main verb in the negative sentences.
- We use the helping verb do or does in the negative sentences.
- ‘Do‘ is used for the plural subjects. ( You do not, We do not They do not, The girls do not, The boys do not).
- ‘Do‘ is used with I. (I do not).
- ‘Does‘ is used with Singular Subjects. (He does not, She does not, It does not, John does not, The girl does not, The boy does not)
- We use ‘not’ after the forms of the verb ‘to be’ – is not, am not, are not.
Structure – Subject + Do/Does + not + Verb I + Object
Examples:
- He does not play here.
- She does not sing in the bar.
- It does not rain in February.
- John does not work at night.
- I do not abuse anyone.
- We do not run on the road.
- You do not swim in the sea.
- The boys do not study in the room.
- We do not hesitate to ask anything from him.
- They do not want to change the terms of the agreement.
- The women of our country take part in the games.
Note – If there is use of ‘never‘ in the sentences, we do not use do or does. We make sentences according to the following structure:
Structure – Subject + never + verb I + object + other words.
Examples –
- He never tells a lie.
- I never beat my child.
- You never speak the truth.
Nobody, No one, Nothing in the sentences
- Nobody comes here.
- No one waits for me.
- Nothing is here.
- Nobody is at the door.
Negative Sentences Structure for the verb ‘to be’
Structure: Subject + to be (is am are) + noun/adjective or other words.
Examples –
- She is not a singer.
- It is not a chair.
- Johnny is not happy today.
- The earth is round.
- I am not a racer.
- You are not a policeman.
- We are not students.
- They are not busy today.
Note: Simple Present Tense in English can be learned by reading these rules. Study these rules carefully and try to use the sentences in daily life.
Rules for Interrogative Sentences –
There are two types of Interrogative Sentences –
Yes-No type questions
The sentences which start with ‘helping verbs’ or ‘auxiliary verbs’ are called Yes-No Type Questions.
Wh-word type questions
The Sentences which start with interrogative words (question words) are called wh-word type questions.
Structure for Yes-No type – Do/Does + Subject + verb I + object + other words + ?
Examples:
- Does he go to see the film?
- Does she write a letter to her friend?
- Does it rain here?
- Does Ram wash his clothes?
- Do I drink water?
- Do you play with me?
- Do they learn English?
- Do we open the windows?
- Does this store open at 7 am daily?
- Does he go to school by bus?
- Do we hate her?
- Does the bus arrive at 6 pm?
Structure for Wh-word – Question word + do/does + subject + verb I + object + other words +?
Examples:
- Why does he go there?
- When does she cook the food?
- Whom do you like?
- How does he swim in the river?
- Where do you live?
- Who calls you?
- Which book do you want to buy?
- How far is your office?

Verb ‘To Be’ Interrogative Sentences
Structure for Yes-No Type: Is/am/are + subject + noun/adjective +?
Examples:
- Is the man busy?
- Are the books on the table?
- Are you happy?
- Am I fit now?
- Is he your relative?
- Am I her teacher?
- Are we satisfied?
- Is this website good for us?
Structure for Wh-word Types Questions: Question word + is/am/are + Subject + noun/adjective or other words + ?
Examples:
- Why are you here?
- Who is there?
- How are you?
- When is your birthday?
- Whose brother is in the USA?
- What is that?
Read also:
Interrogative Negative Sentences
In the interrogative negative sentences, we use ‘not‘ after subject. For example:
- Does she not talk to you?
- Does the boy not cry?
- Why do you not play with me?
- What does he not know?
- When does it not rain?
Emphatic Sentences of Simple Present Tense
To make the emphatic sentences, we put ‘do or does’ according to number and person of a subject. We don’t add s or es to the main verb.
Structure: Subject + do/does + verb I (base form) + object + other words
Examples:
| Non-Emphatic | Emphatic |
| I read a book. | I do read a book. |
| We play cricket. | We do play cricket. |
| You write a letter. | You do write a letter. |
| He sings a song. | He does song a song. |
| It rains. | I does rain |
| They wash the clothes. | They do was the clothes. |
| The man walks. | The man does walk. |
| The boys play. | The boys do play |
Use of Simple Present Tense/Present Indefinite Tense
The Simple Present Tense is used to denote the following: –
To express Habitual Actions –
- He reads the newspaper daily.
- My father gets up every day at four o’clock.
- Ram goes to school at eight o’clock.
- You go to the office daily.
- I get up at 5 a.m. in the morning.
- We visit our village every month.
Note – Some Time expressing adverbs are used to express habitual or repeated actions for example –
- She always goes to the office at nine a.m.
- She often visits us.
- He usually comes here in the morning.
- He never tells a lie.
- He rarely meets me.
To express General Truths (Universal Truths, Principle or Permanent Activities) –
Examples:
- Fortune favors the brave.
- The earth moves around the sun.
- The sun rises in the east.
- Two and two and make four.
- The sun shines by day.
- Water boils at 100°C.
- Honey is sweet.
In the Exclamatory sentences which starts with Here or There –
Examples:
- Here comes the king!
- Here comes the boy!
- There goes the bell!
- There goes the kite!
To express Possession
Examples:
- I have a red hat.
- Mr. Verma owns a big house.
- She has a frock.
- This book belongs to me.
To express feelings, emotions, and mental activities –
Examples:
- I think you are a good singer.
- I believe in God.
- I like mangoes.
- He knows everything about me.
- I hate you.
To express live commentaries –
Examples:
- Sachin runs after the ball, catches it, and throws it on the stumps.
- The bowler throws the ball on the stump.
To express fixed program or event –
Examples:
- The match starts at 5 o’clock.
- The coffee house opens at 8 a.m.
- The chief minister comes here tomorrow.
- Our school reopens in July.
- The flight leaves at 3.30 p.m.
- My brother comes the next day.
Present Indefinite Tewnse is used in Conditional Sentences –
Examples:
- If you work hard, you will pass.
- If he sings well, he will win the competition.
- When he comes here, he will run with you.
- Unless you work, you will not pass.
- She will give you money if she comes here.
To express Past Events (Historic or Graphic present) –
Examples:
- Akbar attacks the enemy and kills.
- The king runs towards the enemy and attacks.
To present the statement or quotation of an author –
Examples:
- Shakespeare says, “We know what we are, but know not what we may be.”
- Alexander Pope says – To err is human, to forgive, divine.
Simple Present Tense Examples
Here are some more examples to understand the Simple Present Tense –
Examples:
- I live in India.
- The Moon goes around the Earth.
- Jack drives a car.
- He does not drive a bus.
- They do not work at night.
- Do you play football?
- He gets up early in the morning.
- The girl reads the newspaper.
- I take my breakfast at 7 a.m.
- Dad says, “I don’t know your friends.”
- I go to the library and read books every day.
- Our gardeners bring fruits for us.
- Shally opens her store at 7 am.
- Does that child cry at night?
- What do you mean?
- What do you think?
Read also –
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Simple Past Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- English Grammar in Hindi
Conclusion
In this post, we have described the simple present tense rules and examples in detail. This tense is also used to describe our daily routine and general time activities. You are advised to read all the rules of the simple present tense (present indefinite tense). Don’t skip any rule. Try to make sentences of this tense and use in your daily life. We have written some examples of this in this post that may give you an idea of making sentences of Simple Present Tense.
- Easy Hindi to English Translation - March 20, 2024
- Present Tense in Hindi – परिभाषा, प्रकार तथा उदाहरण - March 17, 2024
- Personal Pronoun in Hindi – Definition, Examples and Rules - March 8, 2024

Sir simple present tense ka Hind karo na English me hai please 🥺🥺
There is no difference between Simple Present Tense and Present Indefinite Tense Please read in which language you can understand.
You can’t understand English
Thank you so much sir mujhe itna content ek jagah kahi nhi mila thanks again